Biomonitoring
Biomonitoring is measuring environmental chemicals in the human body (tissue and fluids) such as urine and blood
Why conduct Biomonitoring?
- To understand which chemicals are getting into people’s bodies and at what levels (how much) from environmental sources such as air, water, soil, food, and even everyday products
- To track possible trends of chemical exposures in people
- To learn and better understand the relationship between chemical exposure, body burden, and human health
- To help evaluate and make changes to public health policy and interventions (like treatment or removing products from our homes or work) so we can better protect you, your family, and your community’s health
Go to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Biomonitoring Program to find out more about Biomonitoring.
How can Biomonitoring help YOU?
Biomonitoring can help you become more aware of what chemicals are in your body. These chemicals may be coming from the air; the dust around your house; your water, soil, food, or work; or even the products you use daily (such as skin creams or insect repellants). Often, very small amounts of chemicals over a short period of time are not harmful, but it’s important to know what chemicals you come in contact with, so you can make informed healthy choices and reduce chemical exposure over the course of your lifetime.
BiomonitoringNH Studies
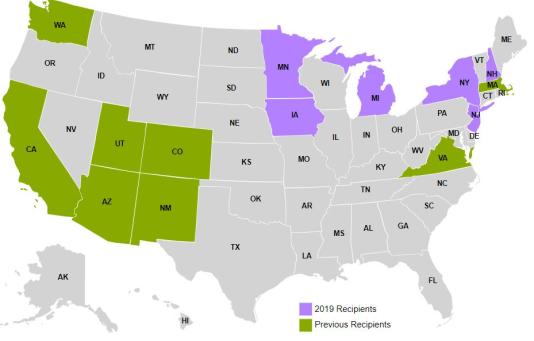
New Hampshire was one of six awardees to receive a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) grant for Biomonitoring in 2019 and one of only two states to be refunded after the 2014-2019 Cooperative Agreement.
Over the next five years, the BiomonitoringNH Program will work on four BiomonitoringNH Studies.
The program is part of the National Biomonitoring Network. This is a group of scientists working to advance biomonitoring using high quality practices to answer environmental health questions.
Biomonitoring Program Links